Emergence of Rajputs: Polity, Economy and Society.
History
- Language
Index
Introduction
The Rajput kingdoms of Northern India emerged as a remarkable collection of states and principalities during the medieval period, spanning from the 6th to the 16th centuries. The Rajputs, a prominent warrior class of the Indian subcontinent, were known for their unrivalled valour, chivalry, and unwavering sense of honour. This article delves into the historical significance of the Rajput kingdoms, shedding light on their geographical extent, political structure, cultural heritage, and economic prowess.
Geographical Diversity: From Deserts to Hills
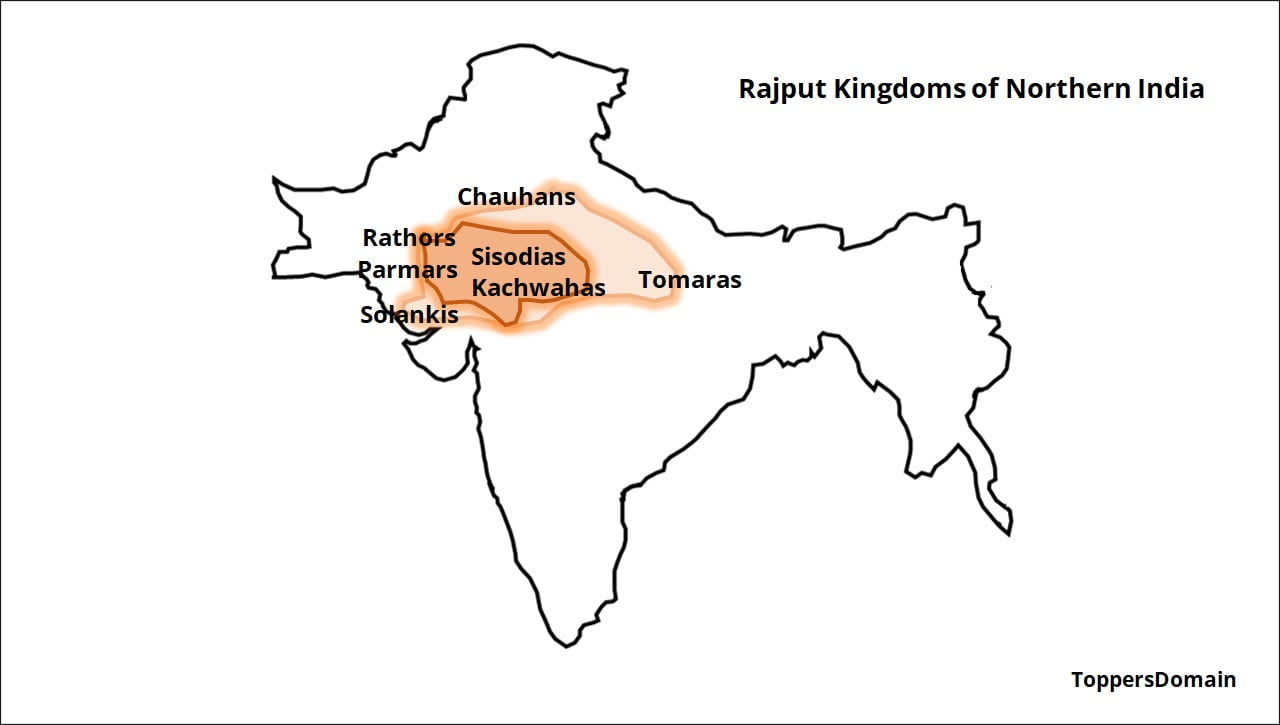
The Rajput kingdoms flourished across a vast expanse, encompassing present-day Rajasthan, parts of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Haryana. Geographically, these territories displayed a rich tapestry of landscapes, ranging from arid deserts to fertile plains and rugged hills. Rajasthan, the heartland of Rajputana, comprised the largest portion of these states, renowned for its sandy terrain, thorny bushes, and limited water sources. These arid conditions significantly shaped the lifestyle and economy of the region, leading to a strong focus on cattle rearing, agriculture, and trade routes.
Rajput Kingdoms
Several Rajput kingdoms emerged and played a significant role in shaping the region's history. These kingdoms were known for their valour, chivalry, and staunch defence of their territories against foreign invasions.
Chauhans of Ajmer and Delhi
The Chauhan dynasty, particularly the rulers of Ajmer and Delhi, held significant prominence during the Sultanate period. Prithviraj Chauhan, the most renowned ruler of this dynasty, fiercely resisted foreign invasions and expanded his kingdom's influence. However, his defeat in the Second Battle of Tarain in 1192 marked a turning point in the region's history.
Rathors of Marwar
The Rathors of Marwar, led by Rao Jodha, established their dominance in present-day Rajasthan. They built the magnificent Mehrangarh Fort in Jodhpur, which stands as a testament to their architectural and military prowess. The Rathors maintained their independence, skilfully navigating through alliances and conflicts with both indigenous and foreign powers.
Sisodias of Mewar
The Sisodias of Mewar, with Chittorgarh as their capital, were renowned for their unwavering commitment to valour and sacrifice. Rana Kumbha and Rana Sanga were among the notable rulers of this dynasty. Chittorgarh Fort became a symbol of Rajput resistance against the Sultanate and witnessed several epic battles.
Kachwahas of Amber and Jaipur
The Kachwahas of Amber, later known as Jaipur, established their rule in the eastern part of present-day Rajasthan. Their strategic alliance with the Mughals allowed them to retain their autonomy while enjoying the benefits of imperial patronage. Amer Fort and Jaipur's City Palace are remarkable architectural marvels attributed to the Kachwahas.
Tomaras of Delhi
The Tomara dynasty ruled over Delhi before the rise of the Sultanate. Anangpal Tomar is considered one of the earliest significant rulers of Delhi. Although their influence declined during the Sultanate period, their contributions to the region's history cannot be overlooked.
Influence and Strategic Importance
The Rajput kingdoms exerted considerable influence over Northern India, owing to their strategic locations along major trade routes. Their involvement in regional commerce was instrumental in fostering economic growth. Furthermore, the Rajputs were renowned for their military prowess, with their states often serving as bulwarks against external invasions. They defended their territories fiercely and forged alliances with neighbouring states to safeguard their interests and maintain stability in the region.
Feudal Polity: A Tapestry of Independent States
The polity of the Rajput kingdoms was characterized by a feudal system, with the king or ruler occupying the pinnacle of the social hierarchy. Assisting the king were council members and advisors who facilitated the administration of the state. The Rajputs valued their independence and autonomy, resulting in a decentralized political structure. Each Rajput state operated as a separate entity, boasting its own governance system and legal framework. However, during times of external threats or shared interests, Rajput rulers frequently joined forces and cooperated with one another.
Culture: Upholding Tradition and Valuing Honour
Culture played a pivotal role in the Rajput kingdoms, permeating every aspect of their existence. Deeply rooted in their traditions, the Rajputs followed a code of conduct known as "Rajput dharma." This code emphasized bravery, loyalty, and honour, and became an intrinsic part of the Rajput psyche. Rajput culture also celebrated martial values, and the practice of chivalry and valour held immense reverence. Elaborate rituals, festivals, and folk traditions showcased the rich cultural heritage of the Rajputs. Art forms such as miniature painting, architecture, and music thrived under their patronage, leaving a lasting legacy.
Economy: An Agrarian Tapestry Enriched by Trade
The Rajput kingdoms boasted a mixed agrarian and trade-based economy. Agriculture served as the backbone, with the cultivation of crops such as wheat, barley, millet, and pulses. The arid landscape necessitated the development of irrigation systems, including step wells (baoris) and canals, to ensure water availability for farming. Moreover, the strategic location of the Rajput states on trade routes connecting Central Asia, the Middle East, and the Indian Ocean facilitated thriving trade and commerce. Levying taxes on goods passing through their territories provided a significant source of revenue. Cities like Jaipur, Jaisalmer, Jodhpur, and Udaipur emerged as prominent trading centres, attracting merchants from across India and beyond.
Challenges and Resilience: Defending Autonomy
Despite their regional autonomy, the Rajput states faced numerous external challenges from various dynasties and empires seeking to expand their territories. The Rajputs fiercely defended their lands and engaged in frequent conflicts with invading forces. They valiantly resisted the Delhi Sultanate, the Mughal Empire, and later the Marathas and the British East India Company. While several Rajput states eventually succumbed to external powers, their resistance and valour left an indelible impact on the history and identity of Northern India.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, the Rajput states in Northern India during the medieval period constituted a glorious chapter in history. Their expansive territories, coupled with their political, cultural, and economic achievements, shaped the region profoundly. The Rajput kingdoms' feudal structure, reinforced by a profound sense of honour and adherence to traditions, stands as a testament to their heritage. Their agrarian economy, complemented by flourishing trade and commerce, contributed to their prosperity. The Rajputs' unwavering defence of their territories against external invasions and their alliances with neighbouring states played a pivotal role in shaping the political landscape of Northern India.