Bhil Tribes
Human Geography
Index
Bhil Tribes
The Bhil tribes are one of the largest indigenous communities of India. They primarily reside in the states of Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Rajasthan and Maharashtra. They have a rich cultural heritage, distinct social norms and a unique economy. Let’s have an overview of the society, culture and economy of the Bhil tribes.
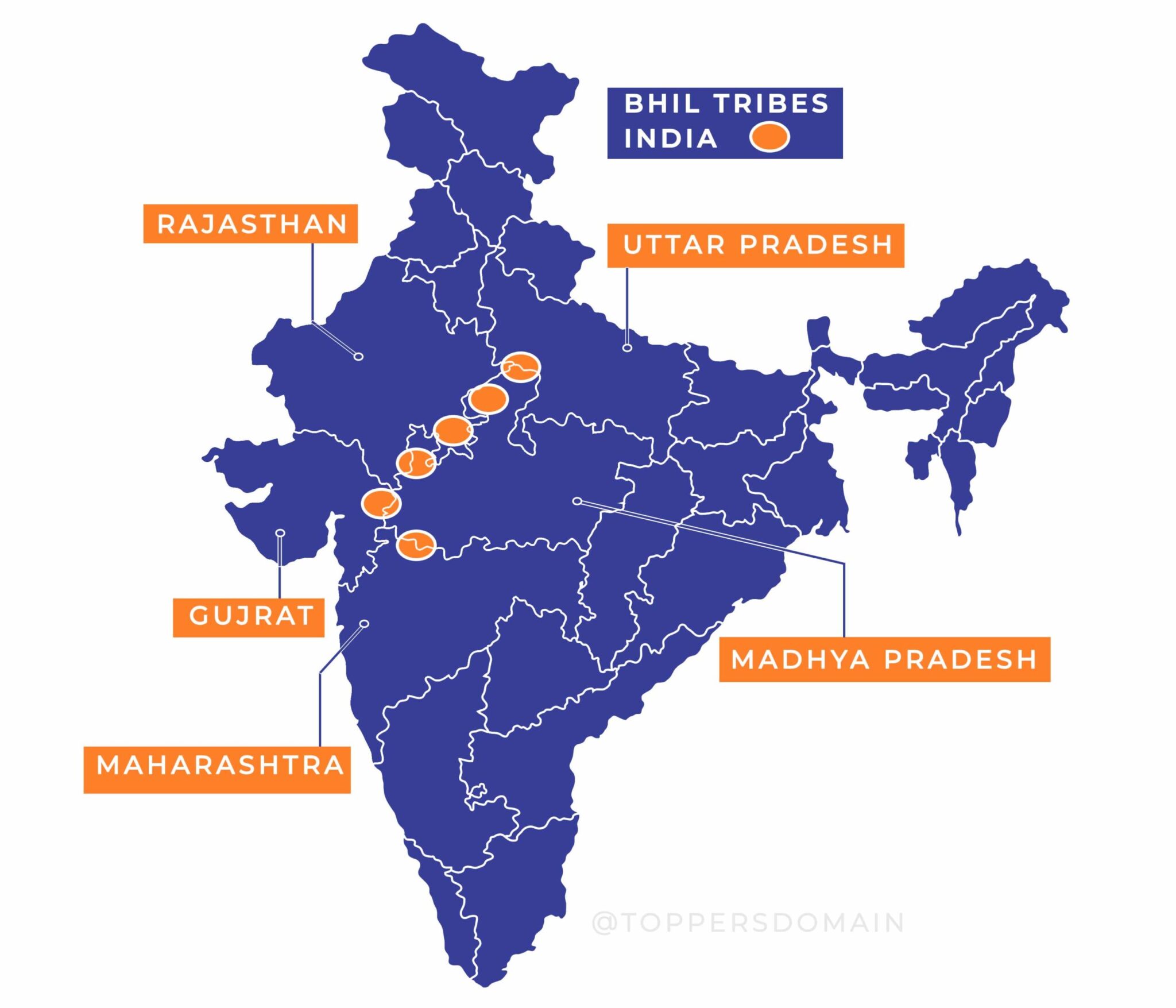
Geographical Distribution
The Bhil tribe is primarily found in the western and central parts of the country. They inhabit various regions of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and also some parts of Uttar Pradesh. Their habitat ranges from arid regions, hilly terrains, dense forests and river valleys. They traditionally live in small settlements in these areas.
Society
The Bhil society is organized into a hierarchical structure, with the headman or the ‘Bhagat’ at the top of the societal pyramid. The Bhagat is responsible for resolving disputes, maintaining social order and overseeing the religious and cultural practices of the community.
The Bhil society is primarily patriarchal, with men holding most of the decision-making powers. However, women do have a say in certain matters such as the selection of a groom.
The Bhil tribes are also known for their unique marriage customs. Traditionally, Bhil men could marry up to seven wives. However, this practice has now been restricted to one wife per husband and Bhil women are expected to remain faithful to their husbands. Marriage within the same clan is prohibited
Culture
The Bhil tribes have a rich cultural heritage, with a unique language, customs and traditions. The Bhil language belongs to the Bhili language (a Western Indo-Aryan language, spoken in west-central India, in the states of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh). This language is widely spoken among the Bhil community. The Bhils have a rich oral tradition and have preserved their stories and legends through songs, dances and music.
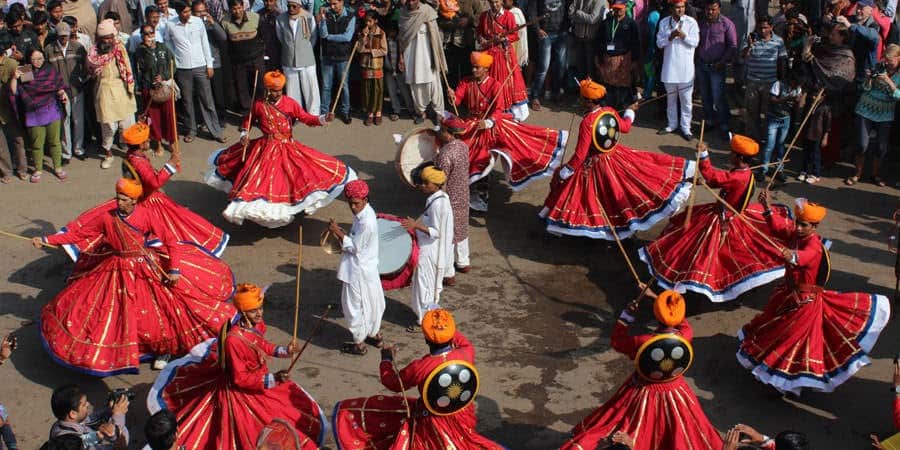
The Bhils are also known for their traditional dance forms. These dances are performed during festivals and other cultural events and involve intricate footwork, colourful costumes and energetic music.
The Bhils are also deeply religious people. They follow a syncretic form of Hinduism, blending their indigenous beliefs and practices with mainstream Hinduism. They worship a range of deities and spirits, including the goddess Kali, who is considered the most important deity among the Bhil tribes.
Economy
The Bhil economy is primarily based on agriculture and forest produce. The Bhils are skilled farmers and cultivate a range of crops such as wheat, maize and millet. They also rear livestock such as cattle, goats and sheep for their own consumption and trade.
The Bhils are also known for their expertise in collecting and processing forest produce such as honey, fruits and medicinal plants. They also practice traditional hunting and fishing methods to supplement their food supply.
In recent years, the Bhil tribes have also been involved in small - scale industries such as handloom weaving, pottery and basketry. The government has initiated several schemes to promote entrepreneurship among the Bhil tribes, such as providing subsidies and training programs.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, the Bhil tribes of India have a unique society, culture and economy. Their hierarchical society (social structure), unique marriage customs and syncretic form of Hinduism distinguish them from other indigenous communities in India. The Bhil language, traditional dance forms and oral traditions reflect their rich cultural heritage, while their expertise in farming, forest produce and small-scale industries form the backbone of their economy. The Bhil tribes have faced several challenges such as poverty, lack of education and discrimination, but they continue to preserve their rich cultural heritage and strive for economic empowerment.
Share
Other Topics
Unit - IV