Linguistic Regions
Human Geography
Index
Linguistic Regions
Linguistic regions refer to areas that are defined by the prevalence of a particular language or group of languages. The world is home to a rich diversity of languages, with over 7,000 languages spoken worldwide.
While it is challenging to categorize the languages of the world into discrete regions, we can broadly classify them based on linguistic families or language groups.
There are several major linguistic regions in the world and each of them is characterized by unique linguistic features and cultural traditions. Some of the major linguistic regions in the world are as follows.
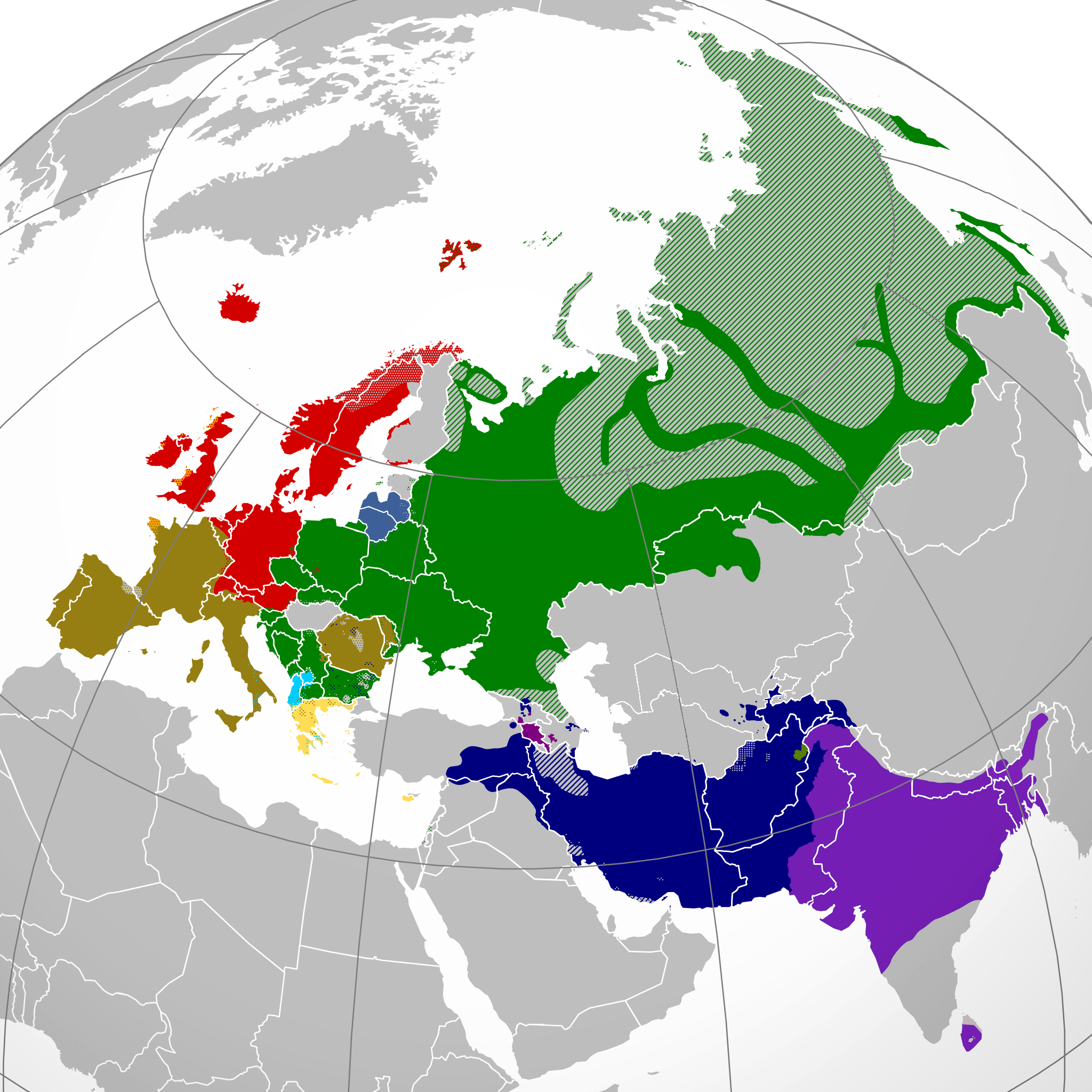
Indo-European Linguistic Region
Indo-European language is one of the largest and most widely spoken language families in the world. It includes over 400 languages spoken worldwide. It is spread across Europe, Asia, Americas and includes languages such as English, Spanish, German, French, Italian, Russian, Greek, Hindi, Urdu and many more. The Indo-European region is also home to many extinct languages such as Latin, ancient Greek and Sanskrit.
Sino-Tibetan Linguistic Region
The Sino-Tibetan linguistic region includes languages spoken in China, Tibet and parts of Southeast Asia. It includes over 400 languages spoken worldwide.
It is the second-largest linguistic family in the world and includes languages such as Mandarin, Cantonese, Tibetan, Burmese and Thai. These are some of the most widely spoken languages in this region.
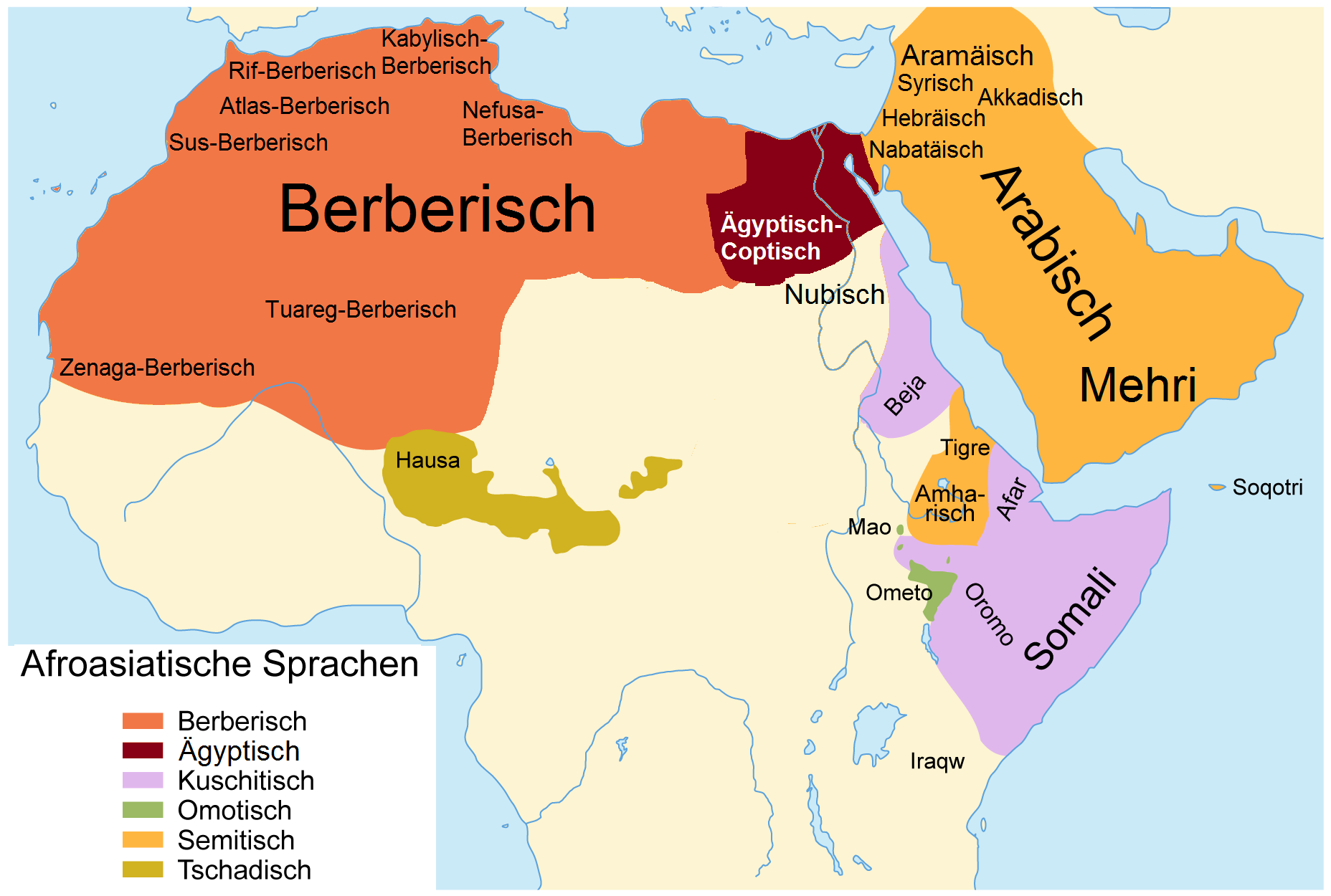
Afro-Asiatic Linguistic Region
The Afro-Asiatic linguistic region includes languages spoken in North Africa, Middle East and parts of East Africa. It is one of the oldest and most diverse linguistic families in the world and includes languages such as Arabic, Hebrew, Amharic, Somali and Berber. The languages in the Afro-Asiatic family share many common features.
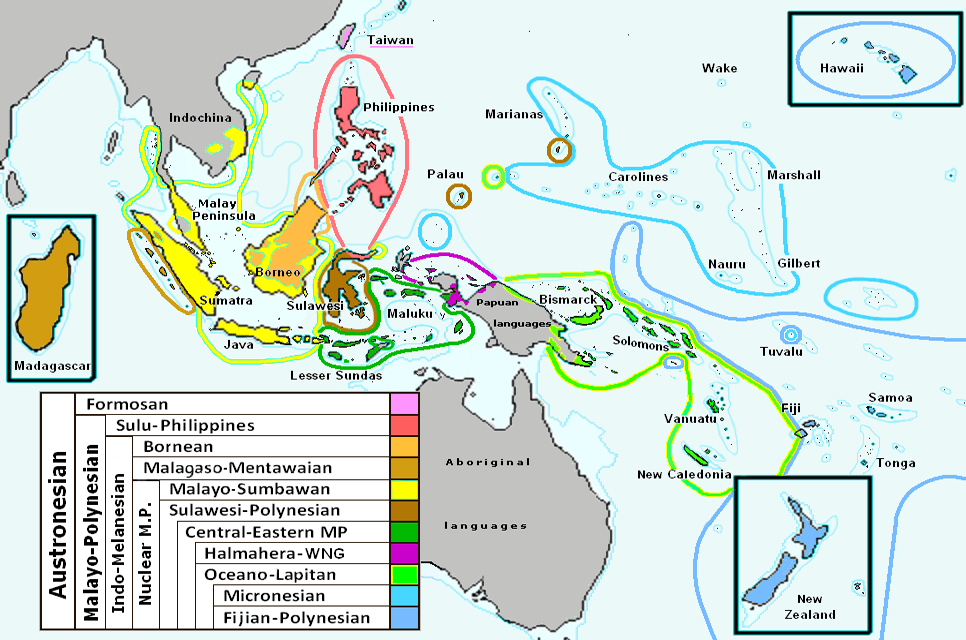
Austronesian Linguistic Region
The Austronesian linguistic region includes languages spoken in Southeast Asia, Pacific Islands and parts of East Africa. It is one of the most widespread linguistic families in the world and includes languages such as Malay, Indonesian, Tagalog and Hawaiian. This linguistic family is also found in Madagascar, off the coast of East Africa. The Austronesian family includes Malayo-Polynesian branch, which includes languages spoken in both the Philippines and Indonesia.
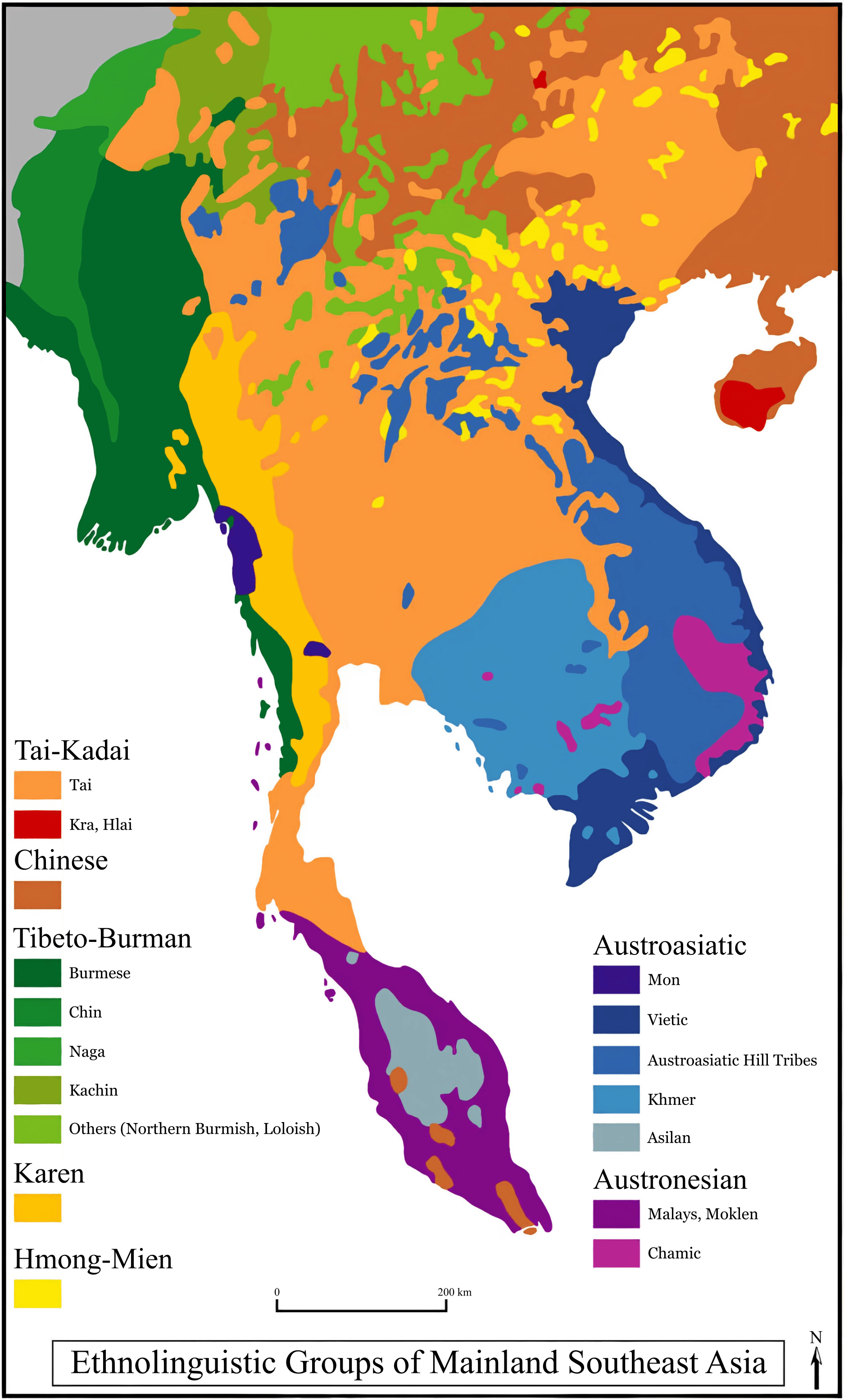
Austroasiatic Linguistic Region
The Austroasiatic language family is mainly spoken in Southeast Asia and includes languages such as Vietnamese, Khmer and Mon.
Niger-Congo Linguistic Region
The Niger-Congo language family is the largest language family in Africa, with over 1,500 languages spoken. This linguistic region includes languages spoken in West and Central Africa. It is the largest linguistic family in Africa and includes languages such as Swahili, Yoruba, Zulu and Hausa.
Dravidian Linguistic Region
The Dravidian linguistic region includes languages spoken in South India and parts of Sri Lanka. It is one of the oldest linguistic families in the world and includes languages such as Tamil, Telugu, Kannada and Malayalam.
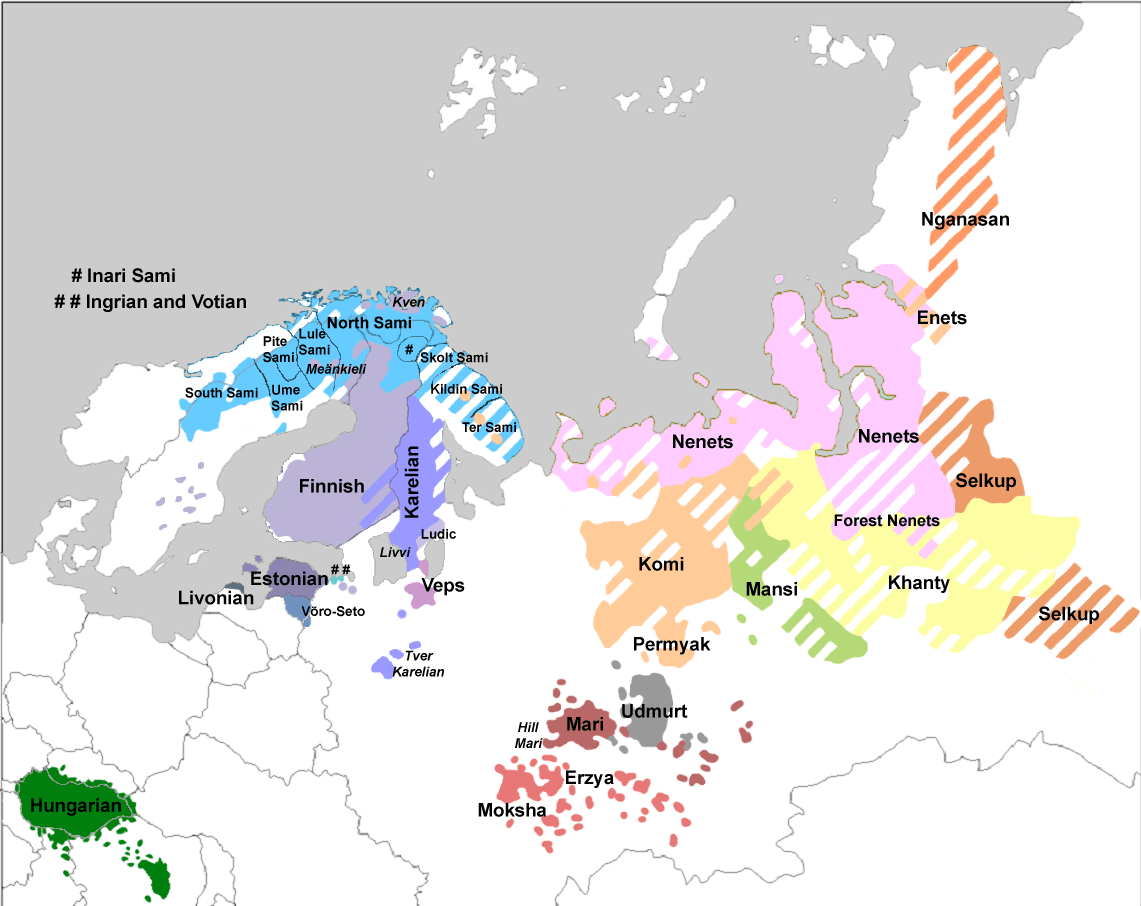
Uralic Linguistic Region
The Uralic language family is mainly spoken in Northern Europe and Asia and includes languages such as Finnish, Estonian and Hungarian.
Altaic Linguistic Region
The Altaic linguistic region covers a broad swath of territory from Eastern Europe to Northeast Asia. The language of Altaic family is mainly spoken in Central Asia and includes languages such as Turkish, Mongolian and Kazakh.
Conclusion :
To conclude one can, say that linguistic regions are geographical areas characterized by a common language or dialect. These regions are defined by the linguistic features that distinguish the language or dialect spoken within them from those spoken in other areas. The boundaries of linguistic regions are often shaped by geographical, historical, cultural, and social factors.
The significance of linguistic regions lies in their ability to provide insight into the diversity and complexity of human language. By examining the unique linguistic features of different regions. Additionally, linguistic regions can provide important information about the history and culture of the people who inhabit them, as well as their relationships with neighbouring communities. The similarities between these languages are the result of language contact and convergence.
Share
Other Topics
Unit - II