Delineation of Planning Regions
Regional Planning & Development
Index
Introduction
Planning regions refer to geographic areas designated for the purpose of strategic urban and regional planning. They are typically defined by government authorities and serve as frameworks for comprehensive development policies and land-use regulations. Planning regions encompass multiple municipalities or districts and aim to promote efficient allocation of resources, balanced growth and coordinated infrastructure development. These regions facilitate collaboration among different stakeholders, such as government agencies, local communities and private sector entities, to address common challenges and achieve sustainable and inclusive development. Through coordinated planning efforts, planning regions foster better spatial organization, infrastructure connectivity and optimized land use to support the socioeconomic needs of the population.
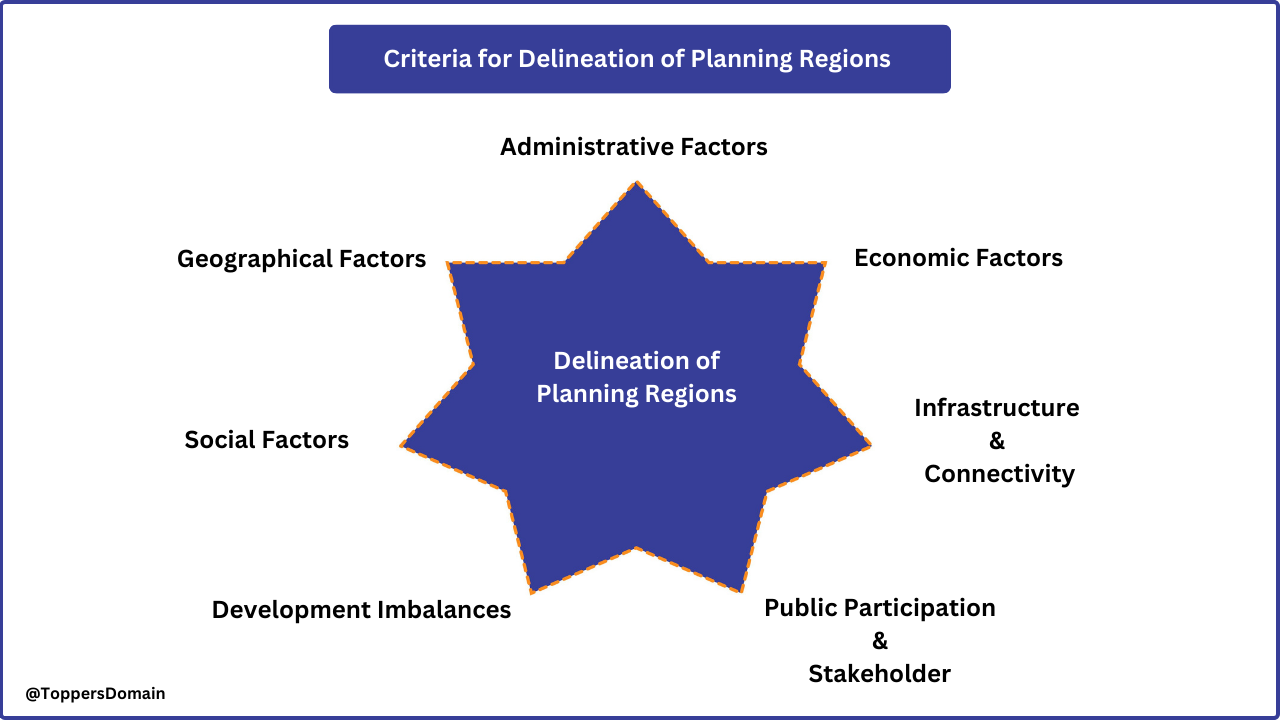
Delineation of Planning Regions
Planning regions are defined areas within the country that are used for effective and coordinated development planning. The delineation of planning regions is an important aspect of regional planning in India. The criteria for delineating planning regions in India are based on various factors, including geographical, economic, social and administrative considerations. These criteria ensure that the planning regions are coherent and representative of the specific needs and characteristics of the areas they encompass.
Geographical Factors
Geographical factors play a crucial role in the delineation of planning regions. It involves considerations such as landforms, climate, natural resources and connectivity. Planning regions are often demarcated based on geographical boundaries such as rivers, mountain ranges, or ecological zones. For example, the Himalayan region, coastal areas, or the arid regions might be identified as distinct planning regions due to their unique characteristics and development challenges.
Economic Factors
Economic factors are also essential in defining planning regions. Economic indicators like GDP, industrial activity, agricultural productivity and employment patterns are considered to identify regions with similar economic characteristics. For instance, regions with high agricultural productivity may be grouped together, while areas with significant industrial activity could form separate planning regions. This allows for targeted and context-specific development planning.
Social Factors
Social factors, including demographic composition, cultural diversity, and social infrastructure, are considered while delineating planning regions. Areas with similar social characteristics and development challenges are often grouped together. This ensures that social development initiatives, such as education, healthcare and social welfare, are tailored to the specific needs of the region's population.
Administrative Factors
Administrative factors are crucial in the delineation of planning regions to ensure effective governance and coordination. Existing administrative boundaries, such as states or districts, may be considered to delineate planning regions. However, the administrative boundaries alone might not always align with the regional development needs. In such cases, smaller administrative units can be merged or divided to create coherent planning regions.
Development Imbalance
Another criterion for delineating planning regions is addressing development imbalances between regions. India is a vast and diverse country with significant regional disparities. Planning regions can be defined to address these imbalances and focus on the underdeveloped or backward regions. This helps in directing resources and development initiatives towards regions that require special attention.
Infrastructure and Connectivity
Infrastructure and connectivity play a vital role in delineating planning regions. The availability of transportation networks, such as roads, railways and airports, is considered to ensure efficient movement of goods, services and people within and across regions. Well-connected regions can be grouped together to facilitate economic integration and development.
Participation and Stakeholder Consultation
Public participation and stakeholder consultation are integral to the delineation process. It is essential to involve local communities, representatives and experts in the decision-making process to ensure the identification of relevant criteria and to understand the unique needs and aspirations of the regions. This participatory approach ensures that the planning regions are inclusive and reflect the aspirations of the local population.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, the delineation of planning regions in India involves a comprehensive analysis of geographical, economic, social and administrative factors. These criteria help in identifying coherent regions with similar development needs and challenges. By considering these factors, planning regions can be formed to facilitate effective and coordinated development planning, addressing regional imbalances and ensuring sustainable and inclusive growth across the country.
Share
Other Topics
Unit - II