Distribution of World Population
Human Geography
Index
Distribution of World Population
The distribution of world population refers to the geographic spread of people across the globe. It is an important indicator of global demography and it provides insights into the factors that shape human settlement patterns.
As of 2021, the world's population is estimated to be around 7.9 billion people. The distribution of the world population is uneven, with some areas being heavily populated while others are sparsely inhabited. In general, the most densely populated regions of the world are in Asia and Africa, while the least densely populated regions are in Australia, North America and parts of South America.
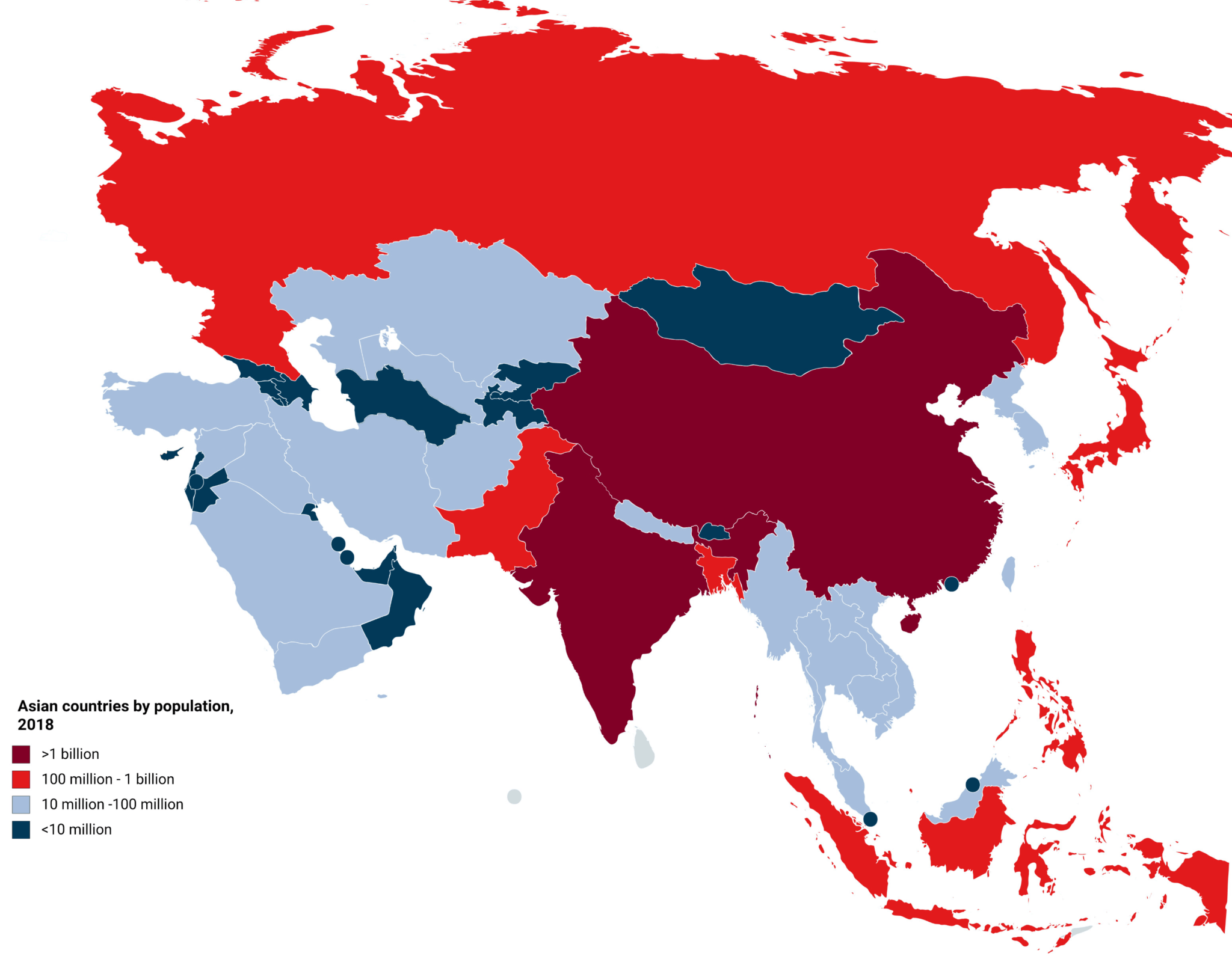
Asia
Asia is the most populous continent. It has over 4 billion people. Within Asia, the most densely populated areas are found in South Asia, particularly in India, which has a population of over 1.3 billion. Other densely populated regions include East Asia, which includes China, Japan and Korea and Southeast Asia.
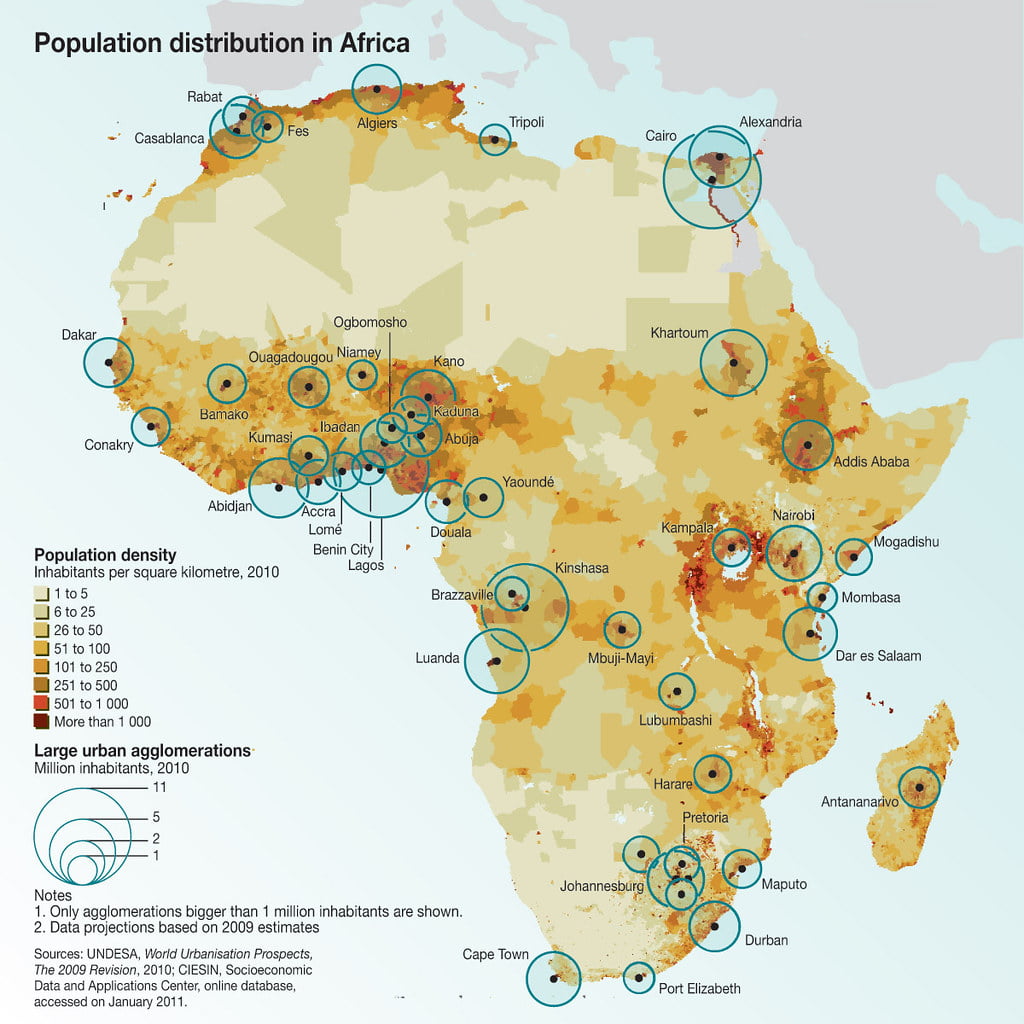
Africa
Africa is the second most populous continent. It has a population of over 1.3 billion people. The continent is characterized by a high birth rate and a young population, which contributes to its rapid population growth. However, population density in Africa is uneven, with some areas being heavily populated, such as the Nile River Valley, while other regions are sparsely inhabited, such as the Sahara Desert.
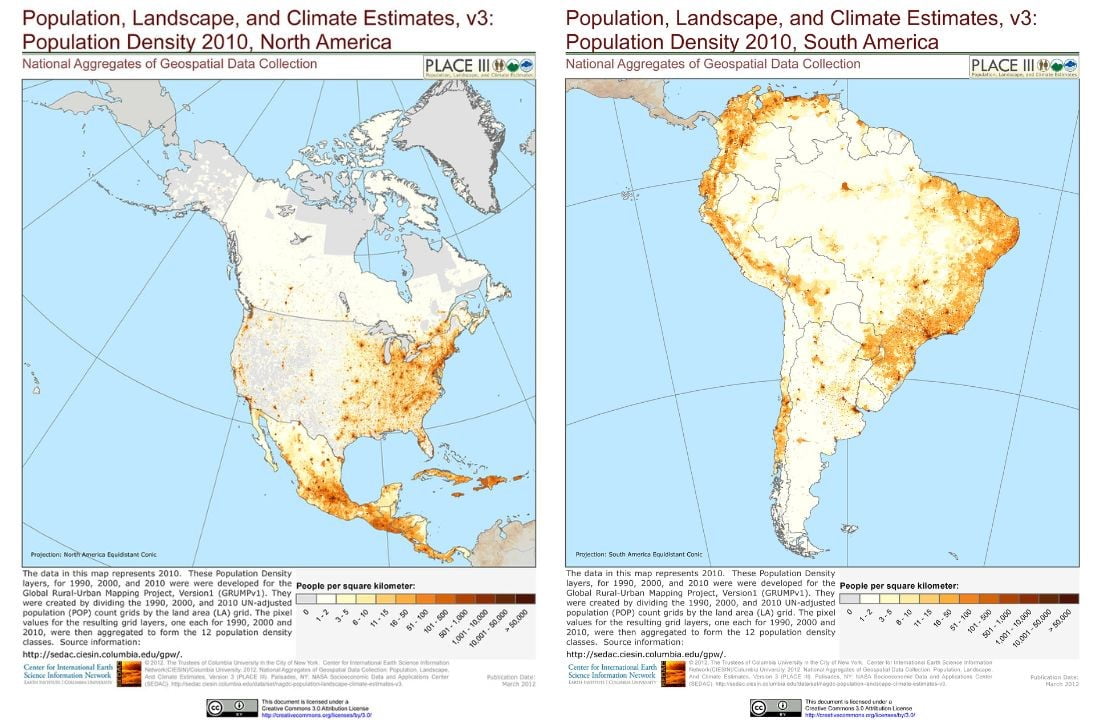
North and South America
North and South America have a combined population of over 1 billion people. The United States is the third most populous country in the world. It has a population of over 330 million. South America is home to over 400 million people. The most populous countries of the region are Brazil, Colombia and Argentina.
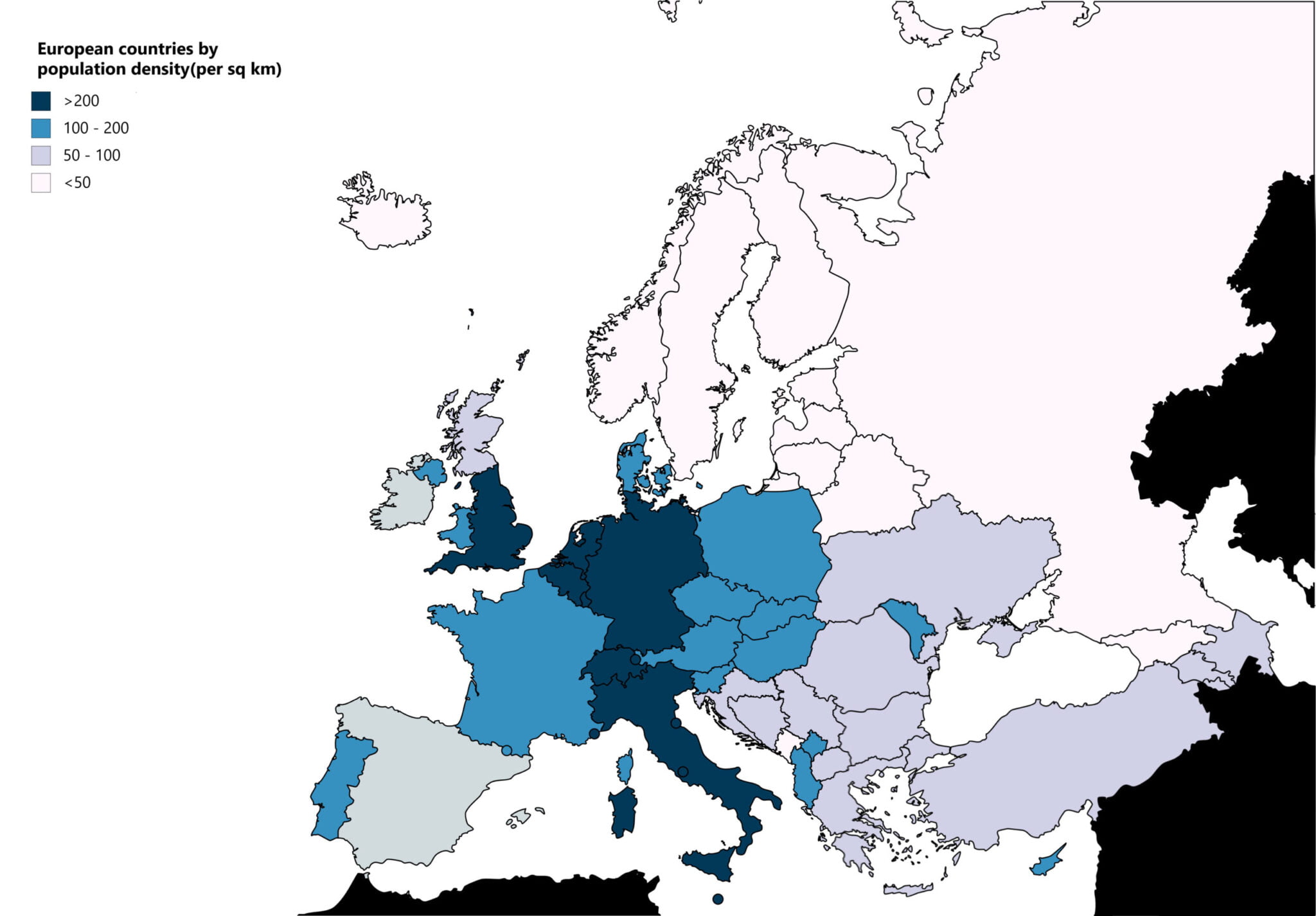
Europe
Europe has a population of over 750 million people. It is the most densely populated continent in the world. The population is concentrated in urban areas, with over 70% of Europeans living in cities. The most populous countries in Europe are Russia, Germany and the United Kingdom.
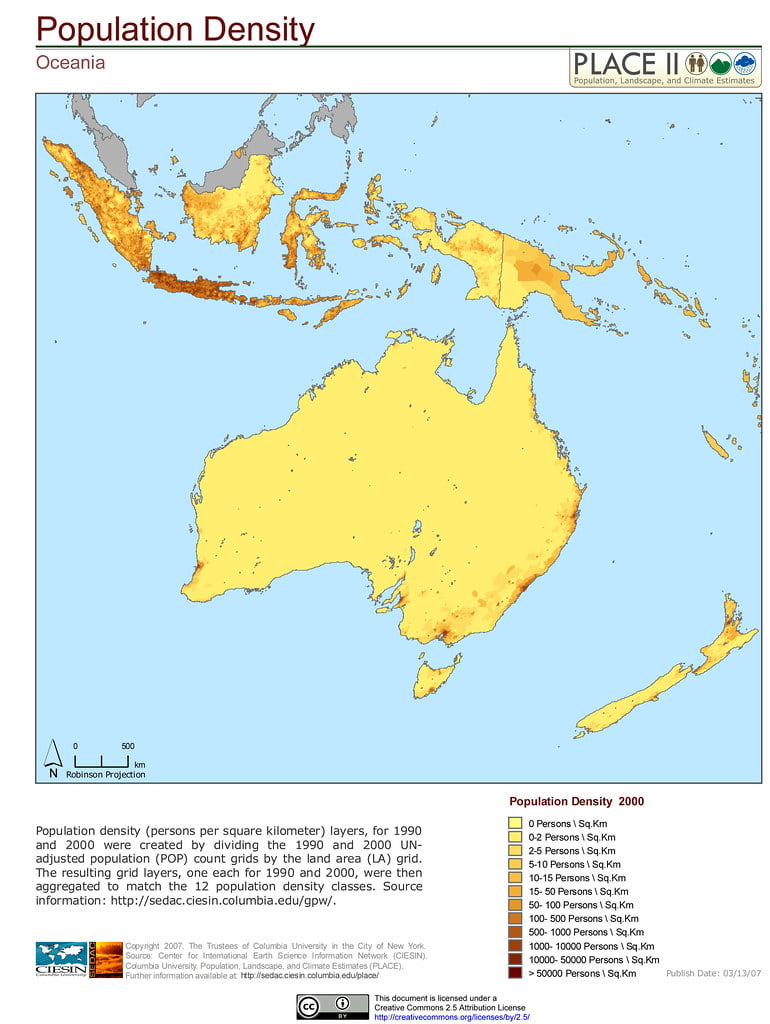
Oceania
Oceania has the smallest population of any continent. It is just over 40 million people. The majority of the population is concentrated in Australia and New Zealand, with smaller populations in other Pacific Island nations.
Distribution of World Population
Understanding the distribution of world population requires examining a range of physical, social, cultural, historical, economic, and environmental factors that have shaped human societies and cultures.
1- Physical Factors
Physical geography plays a critical role in determining the spatial distribution of the world's population. Landforms, such as mountains and deserts create barriers to human settlement, limiting access to resources and making it difficult to build infrastructure. As a result, areas with rugged terrain or inhospitable environments tend to be less populated than areas with more favourable physical conditions.
Climate also influences population distribution. Regions with extreme temperatures or precipitation levels are challenging to inhabit, while areas with a mild and stable climate support large populations. The equatorial region, for example, has a warm and humid climate that dose not supports agriculture, which has led to low population densities in parts of Africa.
2- Cultural Factors
Cultural factors also play a role in population distribution. For example, the cultural and religious values of a society shape settlement patterns. In some cultures, large families are considered desirable, and this leads to a higher population density in certain regions. Religion also influences population distribution, as people are more likely to settle in areas where their faith is the dominant one.
In addition to these factors, political and social factors also play a role in shaping population distribution. Factors such as political instability, war and conflict leads to large-scale migration and population displacement. For example, the ongoing conflict in Syria has led to the displacement of millions of people, many of whom have fled to neighbouring countries.
3- Economic Factors
Economic factors are also essential in determining population distribution. Access to resources, job opportunities and infrastructure attracts people to certain regions. Developed countries with strong economies tend to have higher population densities, as they offer more opportunities for employment and a higher quality of life.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, the distribution of world population is shaped by many factors that interact with each other. Physical, social, cultural, historical, economic and environmental factors all play a role in shaping population distribution. Understanding these factors is essential to address the challenges of population growth and distribution in the 21st century.
Share
Other Topics
Unit - III