Naga Tribes
Human Geography
Index
Naga Tribes
The Naga tribes are indigenous people who inhabit the hilly regions of north-eastern India, mainly the state of Nagaland, but also parts of neighbouring states such as Manipur, Arunachal Pradesh and Assam. They are considered one of the major ethnic groups of the region and are known for their unique culture, customs and traditions and way of life.
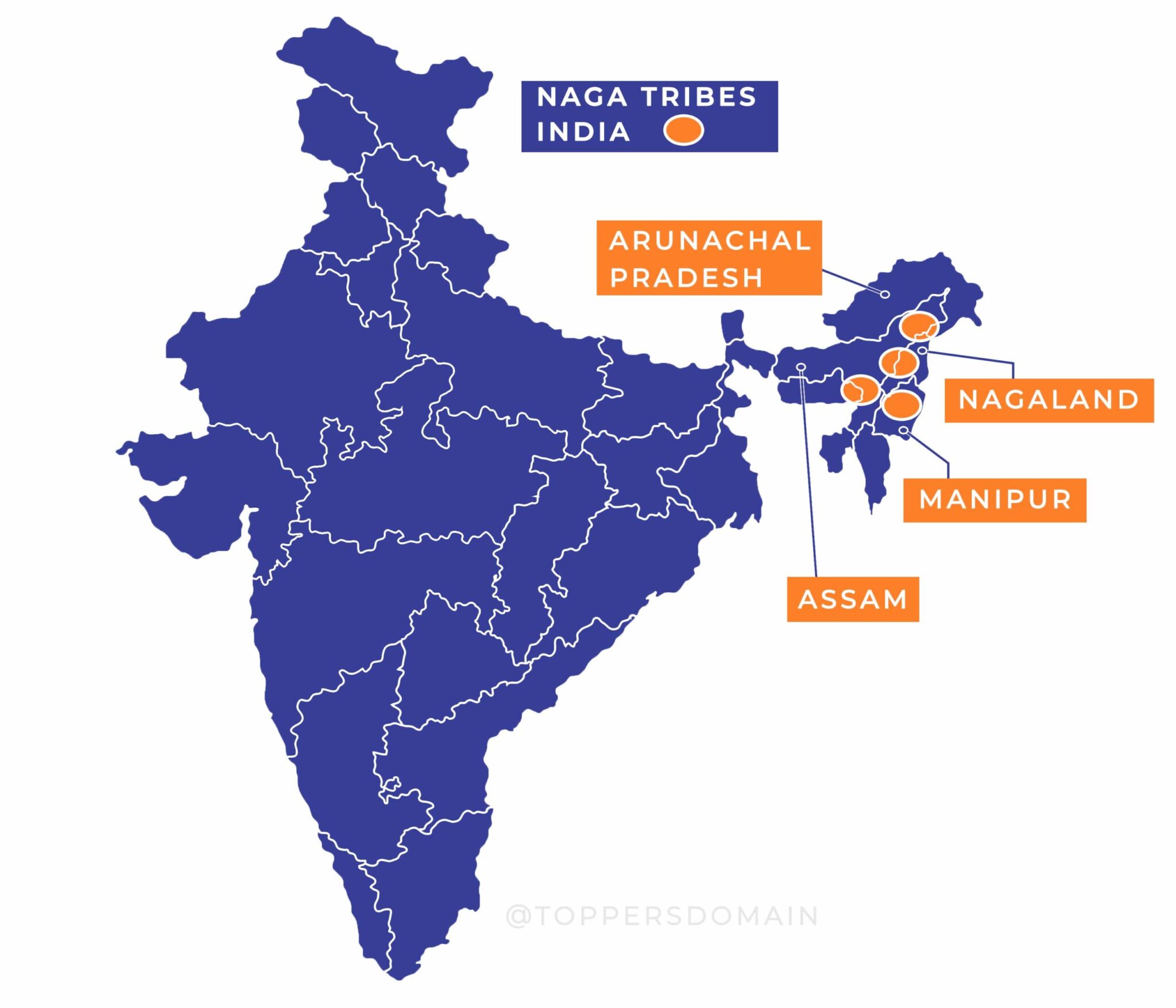
Geographical Distribution
The Nagas live in the hilly regions of north-eastern India, with the majority residing in the state of Nagaland. Nagaland is a landlocked state, surrounded by Assam to the west, Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Myanmar to the east and Manipur to the south. The Naga tribes are spread across various districts in Nagaland, including Kohima, Dimapur, Mokokchung, and Wokha. The terrain is mostly hilly and mountainous, with dense forests and rivers. The climate is tropical, with heavy rainfall during the monsoon season.
Society
There are 16 major tribes and numerous sub-tribes that make up the Naga community. Each of them has their own distinct culture, language and customs. The major tribes include the Angami, Ao, Chakhesang, Chang, Khiamniungan, Konyak, Lotha, Phom, Rengma, Sangtam, Sumi and Yimchunger. The tribes have their own unique dialects and languages, but English is widely spoken and understood.
Traditionally, the Nagas were a warrior society, with a strong emphasis on bravery and honour. Each tribe had its own unique social organization, with the village being the basic unit of social structure.
They have a matrilineal society where inheritance and succession pass through the mother's line, and women play a crucial role in decision-making and governance.
The village council, made up of elders, played an important role in decision-making, with the chief being the ultimate authority.
Culture
The Nagas have a strong sense of community and are known for their hospitality and warmth towards visitors. They are predominantly Christian and have their own unique blend of Christianity that incorporates traditional beliefs and practices.
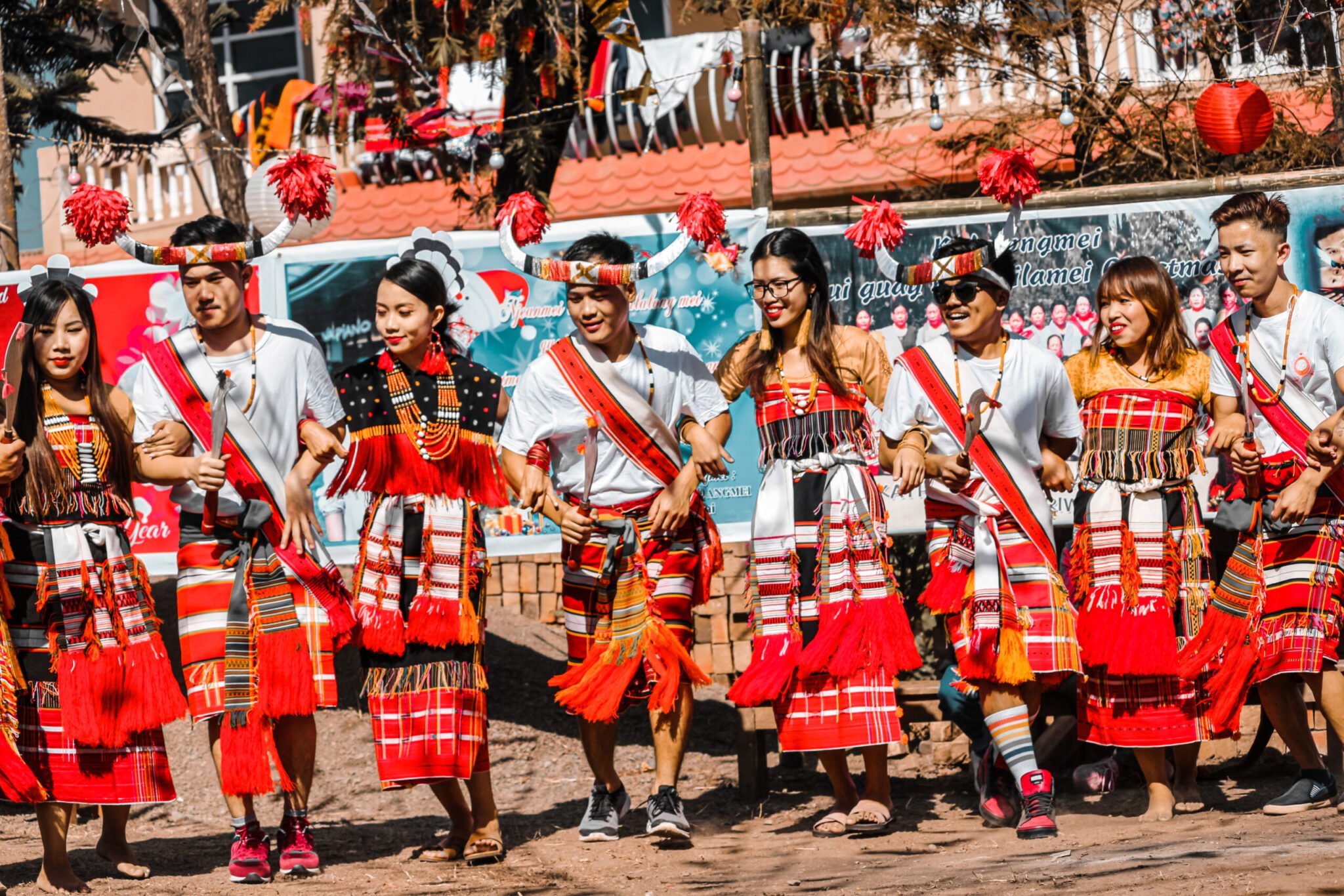
The Nagas are known for their rich and diverse culture, which is reflected in their art, music, dance and festivals. The Naga people are skilled artisans and their handicrafts include bamboo and cane products, wood carvings and hand-woven textiles. They are also known for their distinctive dress, which varies according to tribe and gender. The Naga traditional dress for men is a sleeveless coat, while women wear a wrap- around skirt with a shawl.
The Nagas are also famous for their music and dance. The traditional dances include the warrior dance, performed by men and the bamboo dance, performed by women. The Hornbill Festival, held annually in Nagaland, is a celebration of Naga culture and tradition and is a major tourist attraction. The festival features cultural performances, traditional sports and a food fair showcasing Naga cuisine.
Economy
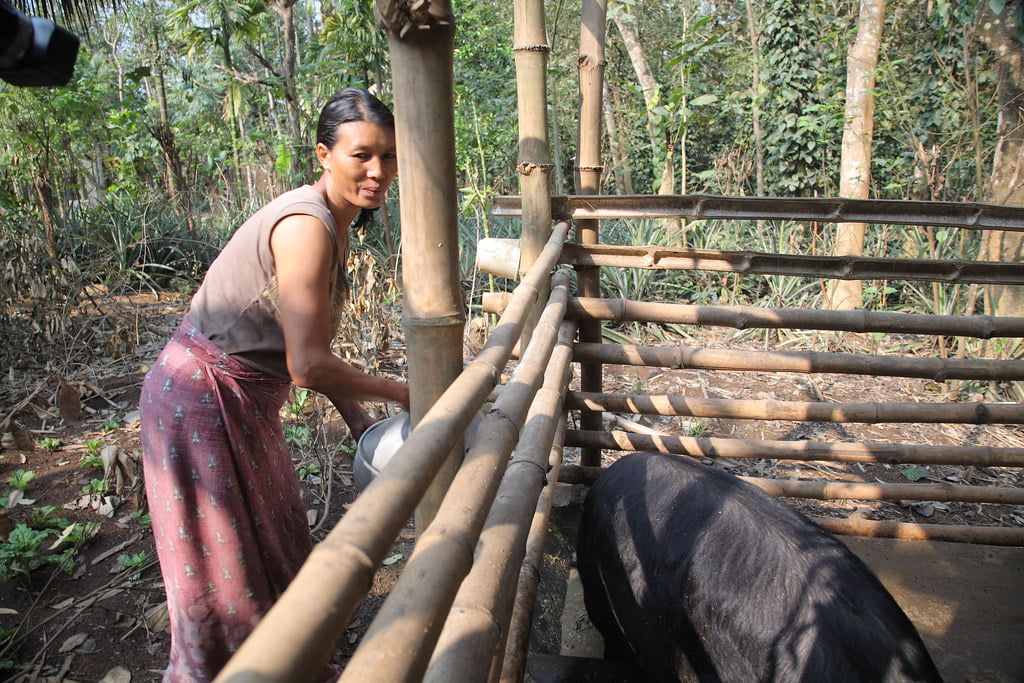
Traditionally, the Nagas were an agrarian society, with agriculture being the mainstay of their economy. The major crops grown include rice, maize, millet, and vegetables. They also cultivate fruits, and spices like ginger and turmeric. Livestock rearing, fishing, and hunting are also important economic activities.
Traditionally they used to practice shifting cultivation or jhum, where the land is cleared by burning the forest and the ash is used as fertilizer.
In recent times, however, the economy of Nagaland has undergone a significant transformation, with the development of industries such as tourism, handicrafts and textiles. The state government has taken several initiatives to promote tourism. Nagaland is now a popular destination for adventure tourism and cultural tourism.
Conclusion :
In conclusion one can say, the Naga tribes of India have a rich and diverse culture, with a strong emphasis on bravery and honour. They are skilled artisans and are known for their unique handicrafts, music and dance.
The Nagas were traditionally an agrarian society, but the economy has now diversified to include industries such as tourism, handicrafts and textiles. They have also started to leverage their unique culture and natural beauty to attract tourists, with initiatives like homestays, adventure tourism, and cultural tours.
The Nagas continue to face several challenges, including socio-economic inequality and conflict, but their resilience and determination have enabled them to preserve their culture and traditions.
Share
Other Topics
Unit - IV