Population Composition
Human Geography
Index
Population Composition
Population structure refers to population characteristics. It refers to the distribution of a population according to various characteristics, such as age, sex, race, ethnicity, education, income, and occupation. In fact, a statistical division of population on the basis of these characteristics is called population structure. It is an important element in understanding the social, economic and cultural characteristics of a population.
By analysing population structure, researchers can identify trends, patterns, and disparities in the population. By studying population composition, policy makers can gain insight into issues such as social and economic inequality and public health, etc. Furthermore, population structure can have important effects on social cohesion and political stability. For example, racial and ethnic disparities can lead to social unrest and political instability.
Some of the different aspects of population composition include:
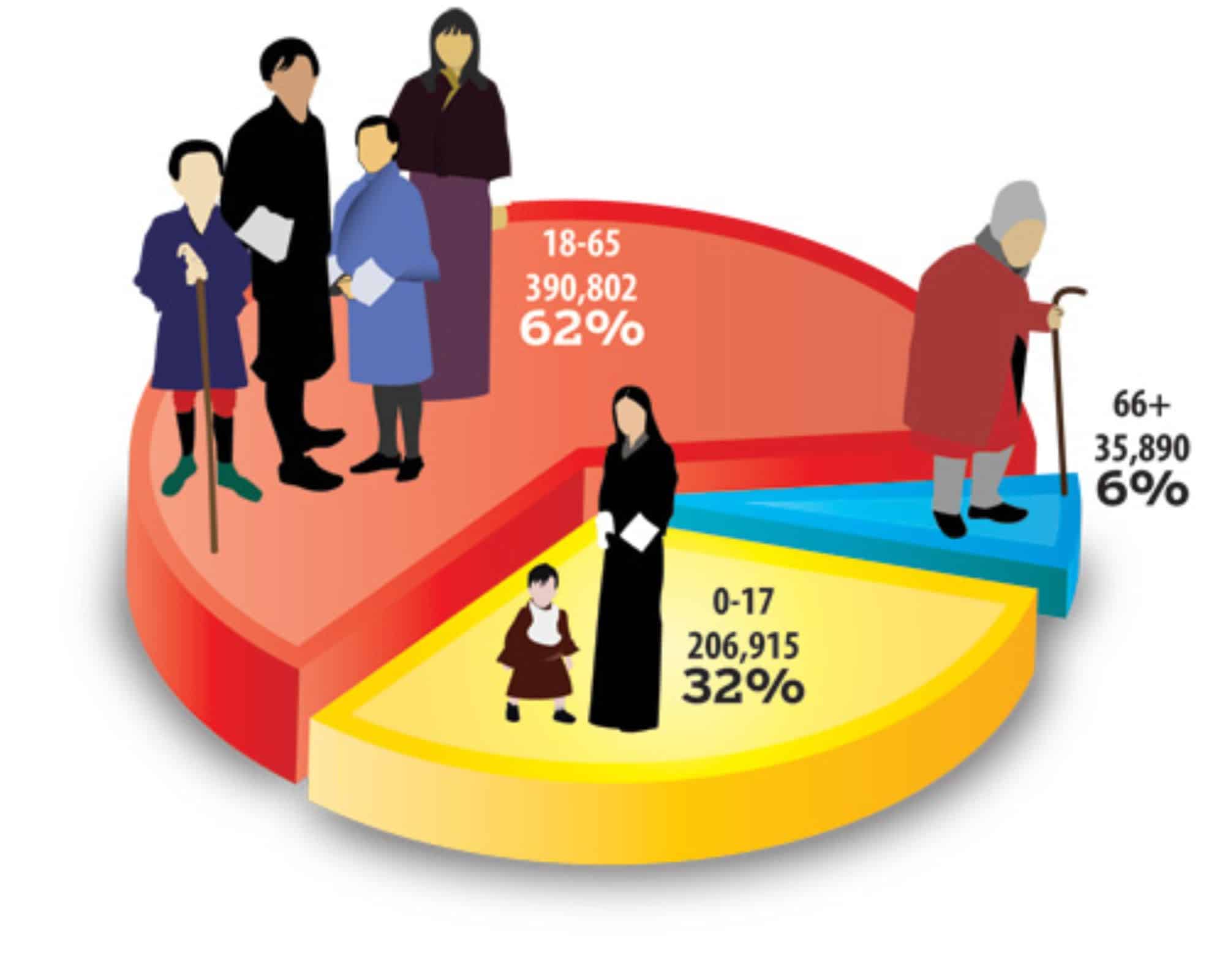
1- Age Composition
Age is a critical factor because it influences various aspects of a person's life, including their education, employment opportunities, health and economic status. The age composition impacts education and the labour force. It is an important factor in determining its social and economic characteristics. A population with a high proportion of young people may have different needs and priorities than a population with a large elderly population. Age also plays a role in workforce participation, retirement and healthcare needs.
2- Sex Composition
Gender or the sex composition of a population refers to the proportion of males and females. It plays a crucial role in shaping various aspects of social life, including the division of labour, family roles and even political participation. This can have implications for issues such as gender equality, family structure and healthcare needs. Understanding gender differences in employment, wages, and educational attainment is critical for policymakers seeking to address gender inequalities in society.
3- Race and Ethnicity
Race and ethnicity are important components of population composition, as they have social, economic and political implications. Racial and ethnic disparities in areas such as education, employment, and healthcare can have long-lasting effects on individuals and communities.
Racial and ethnic disparities in health, education and employment can have significant implications for the overall well-being of a society and economic development. Understanding these disparities is critical for policymakers who seek to address racial and ethnic inequalities.
4- Educational Composition
Education levels are an important aspect of population composition, as they can influence economic outcomes such as income and employment. High levels of education are also associated with better health outcomes and increased social mobility. Apart from that a population with high levels of education and skills is more likely to attract businesses and investment, while a population with a low-skilled workforce may struggle to compete in the global economy.
5- Income and Occupational Composition
Income and occupation are important components of population composition. It can provide insights into the economic status of a population. Income levels and occupational distribution can also have implications for issues such as poverty, social mobility and economic development.
Socioeconomic status is a significant determinant of health, as individuals with lower socioeconomic status tend to have worse health outcomes than those with higher status. Understanding the socioeconomic and religious composition of a population can help policymakers design interventions and policies that target those in need.
Significance of Population Composition
The significance of population composition lies in its ability to inform policy and decision-making. By understanding the social, cultural and economic characteristics of a population, policymakers can design targeted interventions and programs to address specific needs and challenges. For example, a population with a high proportion of elderly individuals may require specialized healthcare services, while a population with low levels of education may require targeted education and job training programs.
- Also read this
Age and Sex Composition of Population (India)
The age and sex composition of a population refers to the distribution of people in a given area according to their age and gender. In other words, it is the distribution of people according to their age and gender. This information is essential for understanding the health, education, economic and social needs of a population. India is the second most populous country in the world with a population of over 1.39 billion as of 2021. (Now it is the most populous country of the world.) Here are some of the details of the age and sex composition of the Indian population...... Continue →
Share
Other Topics
Unit - III