Population Growth
Human Geography
Index
Population Growth
The history of population growth can be traced back to the early stages of human evolution. However, the rate of population growth has been far from uniform throughout history. There have been several periods of exponential growth and some periods of stagnation or even decline.
During the early history, population growth during this period was slow and steady with birth rates roughly equalling death rates. However, with the development of agriculture, population growth began to accelerate. During the Industrial Revolution, population growth began to accelerate at an unprecedented rate. Advances in technology and industry led to an increase in food production, and transportation. This allowed for larger populations to be sustained. Over the time, improvements in healthcare also contributed to population growth. Advances in medicine, sanitation and public health led to longer lifespans and lower infant mortality rates. This in turn led to increased population growth.
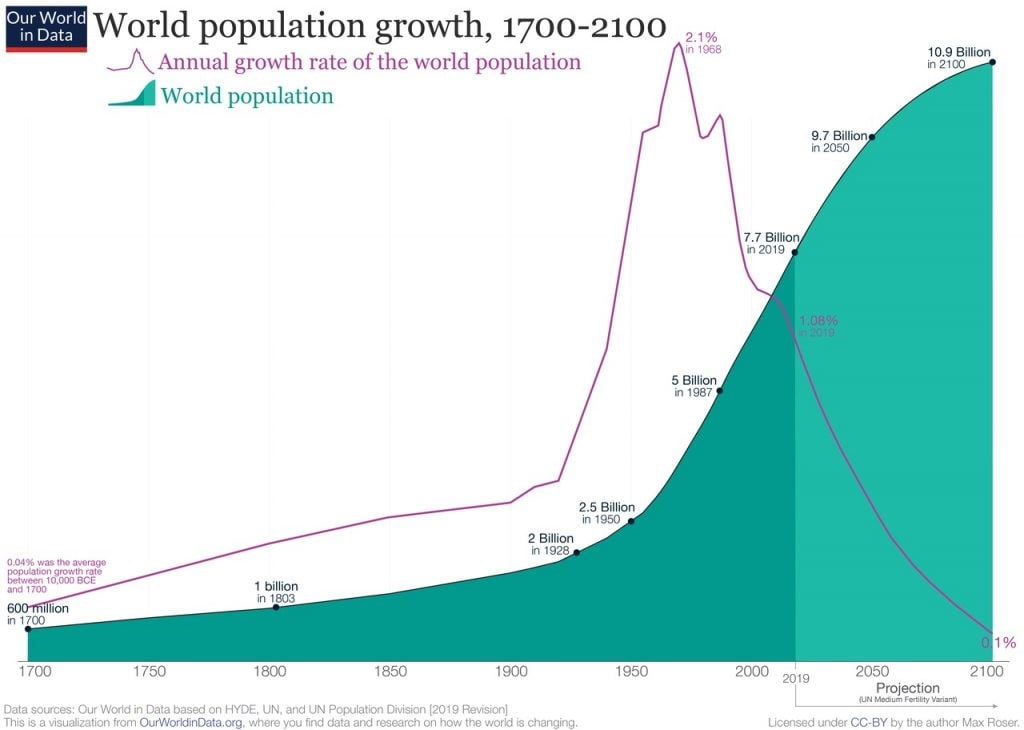
The recent history of population growth can be characterized by exponential growth over the last two centuries. The period between the 18th and 21st centuries saw a significant increase in population growth. The world population was estimated at 1 billion in 1800. It increased from 1.6 billion in 1900 to 7.9 billion in 2021. The world's population projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050.
Factors Contributing to Population Growth
1- Economic Factors
Economic factors, such as increased agricultural productivity has played a critical role in population growth. Advances in crop production and technology have led to significant increases in food production worldwide. This has led to significant improvements in nutrition and overall health and has helped to support a growing population.
2- Technological Advancements
One of the most significant factors contributing to population growth is technological advancements in medicine and improved public health. Improvements in medical treatments, such as vaccinations, antibiotics and surgical techniques, have significantly reduced mortality rates and increased life expectancies. This has contributed to a growing population of older individuals, who are living longer than ever before.
Advances in sanitation, clean water and disease control have significantly reduced mortality rates worldwide. This has led to longer life expectancies, particularly in developing countries, where public health infrastructure has improved significantly over the past few decades.
3- Cultural and Social Factors
Cultural and social factors, such as religious beliefs and attitudes towards family size, also contribute to population growth.
Changes in cultural and social attitudes have also contributed to population growth. In many parts of the world, large families have traditionally been seen as a sign of wealth and prosperity. However, as economic and social conditions have improved, the desire for larger families has decreased. In addition, access to contraception and family planning services has become more widespread, giving individuals greater control over their reproductive choices.
4- Political Factors
Political factors, such as government policies on immigration and family planning, can influence population growth. For instance, countries with strict family policy have experienced decline in population. On the other hand, countries with more liberal immigration policies tend to experience higher population growth rates.
- Challenges of Rapid Population Growth
Despite the many benefits of population growth, there are also several challenges associated with rapid population growth. One of the most significant challenges is the strain it places on natural resources, including water, food and energy. As the population continues to grow, there is a growing demand for these resources, which can lead to depletion of resources and environmental degradation.
In addition, rapid population growth can also lead to overcrowding and urbanization, which can create significant social and economic challenges. This includes increased traffic congestion, housing shortages and unemployment.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, while population growth has brought many benefits, it has also created significant challenges for society. As we move forward, it will be essential to develop strategies to address these challenges while continuing to support a growing population.
Share
Other Topics
Unit - II