Trends and Patterns of World Urbanization
Human Geography
Index
Trends and Patterns of World Urbanization
Urbanization is the process of population concentration in cities and towns and it is a defining feature of modern civilization.
Over the last few centuries, the world has experienced an unprecedented level of urbanization, with an increasing number of people moving from rural areas to cities. It is driven by factors such as industrialization, globalization and demographic changes. On the other hand, it has significant impacts on societies and the environment. As this process involves socioeconomic changes, both in rural and urban areas, as well as changes in the physical landscape of cities.
The trends and patterns of world urbanization are a critical area of study as they have significant implications for social, economic and environmental sustainability.
Trend - I
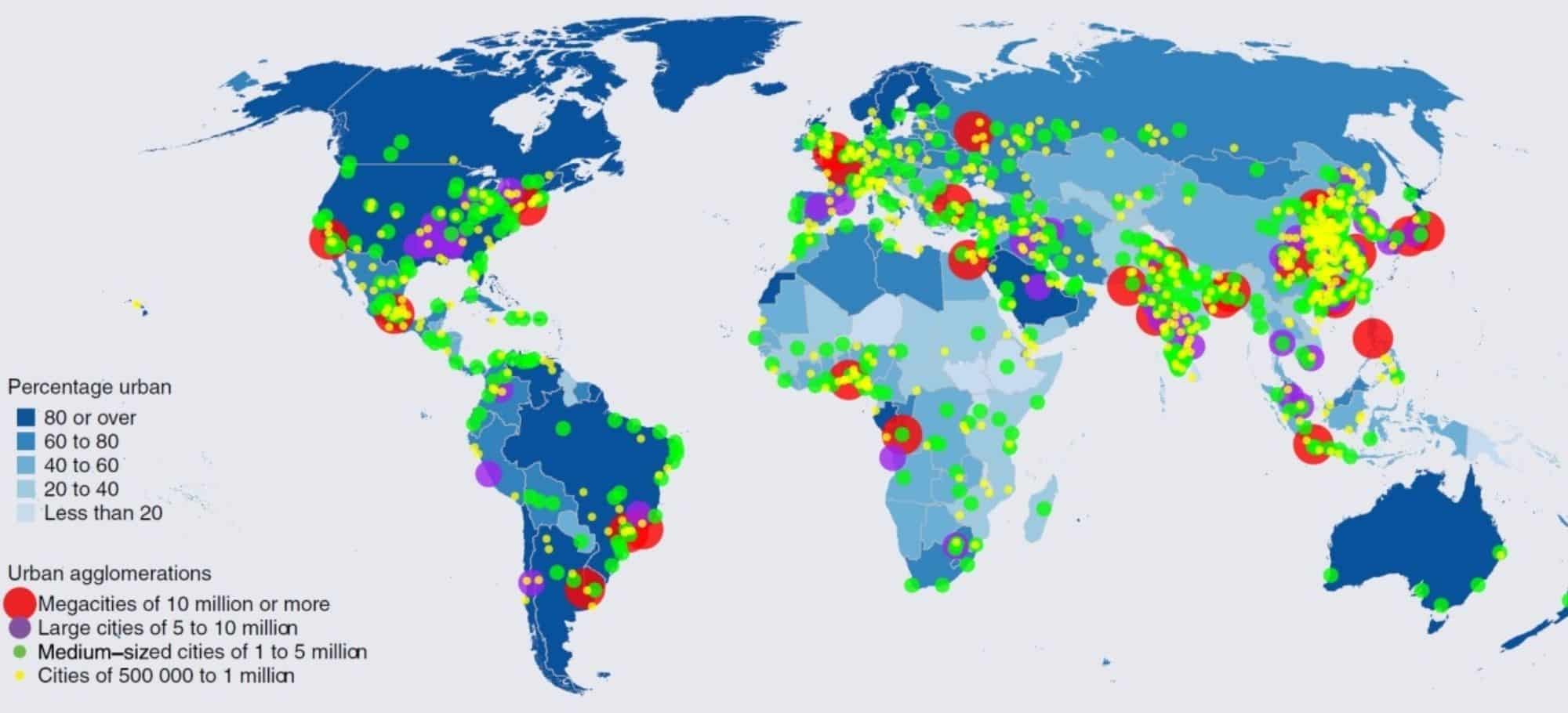
One of the most notable trends of world urbanization is the rapid increase in the world's urban population. According to the United Nations (UN), the world's urban population surpassed the rural population in 2007, and by 2050, it is expected to reach 68% of the global population. This growth is most evident in developing countries, where rate of urbanization has been the highest. For example, in Africa, the urban population has grown from 15% in 1960 to 43% in 2021, while in Asia, it has grown from 17% in 1960 to 52% in 2021. This trend is expected to continue as more and more people migrate to cities in search of better economic opportunities and improved living standards.
Trend - II
Another trend of world urbanization is the emergence of megacities. These are the cities with populations of more than 10 million people. The number of megacities has grown rapidly in the last few decades, from just three in 1975 to 33 in 2021. Most of these megacities are located in developing countries, with Tokyo being the only acceptation. The growth of megacities has significant implications for urban planning and management, as the concentration of such large populations in a small area leads to environmental degradation, social inequality and economic inefficiencies.
Trend – III
A third trend of world urbanization is the increasing number of urban poor. While cities have long been seen as centres of economic growth and opportunities, they have also become centres of poverty, inequality and exclusion. According to the UN, the number of slum dwellers in the world's cities has grown from 650 million in 1990 to over 1 billion in 2021. The growth of slums is a result of a lack of affordable housing, inadequate infrastructure and insufficient access to basic services such as water and sanitation. Addressing the issue of urban poverty requires a concerted effort from policymakers, urban planners and civil society to ensure that cities are inclusive and equitable.
Trend – IV
A fourth trend of world urbanization is the impact of climate change on urban areas. Urban areas are responsible for a significant proportion of global greenhouse gas emissions. They are also particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Climate change is expected to increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as floods, droughts and heatwaves. It is expected to have a significant impact on urban populations. Urban planning and management must take into account the potential effects of climate change to ensure that cities are resilient and adaptive.
Trend – V
Finally, a pattern that has emerged in world urbanization is the increasing importance of cities as engines of economic growth. Cities are centres of innovation, creativity and productivity. These cities have become critical nodes in the global economy. According to the McKinsey Global Institute, 600 cities are expected to generate 60% of global GDP by 2025. This trend highlights the importance of investing in urban infrastructure, education and innovation to ensure that cities can continue to drive economic growth and prosperity.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, the trends and patterns of world urbanization are complex and multifaceted, with significant implications for social, economic and environmental sustainability. While urbanization has brought many benefits, it has also presented significant challenges, such as urban poverty, environmental degradation and social inequality. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from policymakers, urban planners, and civil society.
Share
Other Topics
Unit - III